Evaluation and Optimization: IoU, Non-max Suppression, Anchor Boxes
Intersection over Union (IoU)
Intersection over Union (IoU) is a metric used to evaluate the accuracy of an object detector on a particular dataset. It measures the overlap between two bounding boxes:
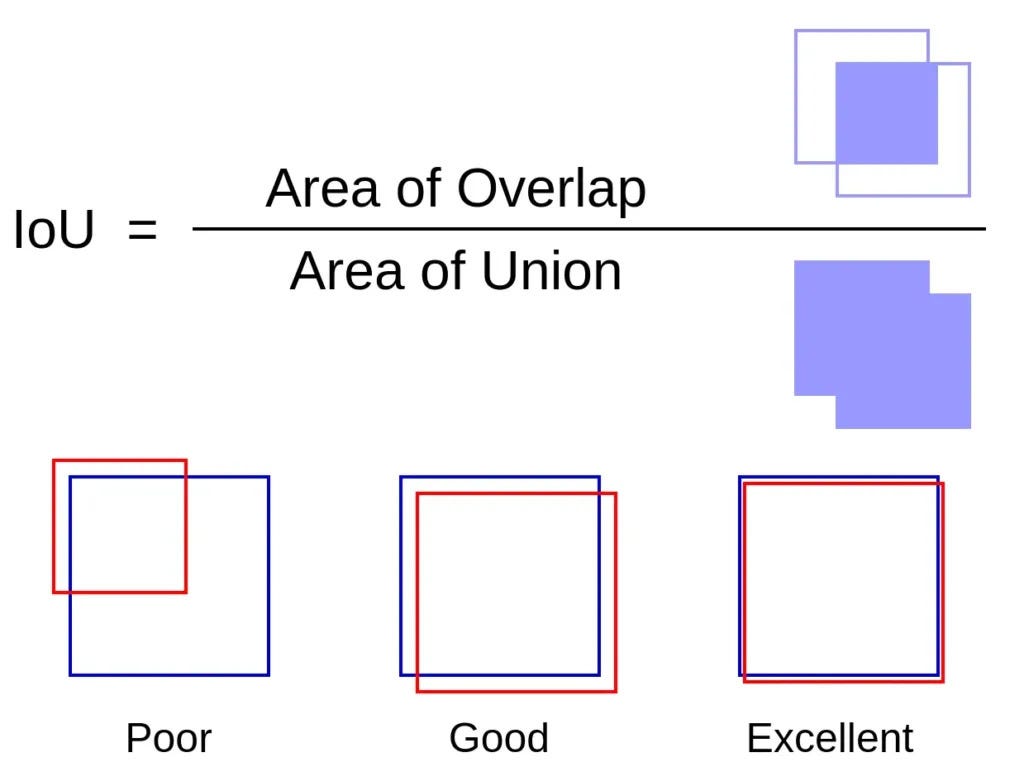
- The predicted bounding box
- The ground-truth bounding box
Mathematical Definition
If is the predicted bounding box and is the ground truth bounding box:
- : perfect overlap
- : no overlap
Example
Suppose:
- Predicted box: top-left = (50, 50), bottom-right = (150, 150)
- Ground truth: top-left = (100, 100), bottom-right = (200, 200)
The overlapping area is a square from (100, 100) to (150, 150) → 50x50 = 2500
Total area:
- Predicted:
- GT:
- Union:
So,
Use in Training and Evaluation
- In training, you may ignore detections with IoU < 0.5
- For evaluation, mAP (mean average precision) uses IoU thresholds (e.g., 0.5 or 0.75)
Non-max Suppression (NMS)
Why Do We Need It?
Object detectors often output multiple overlapping boxes for a single object. NMS filters out redundant boxes by keeping the one with the highest confidence score.
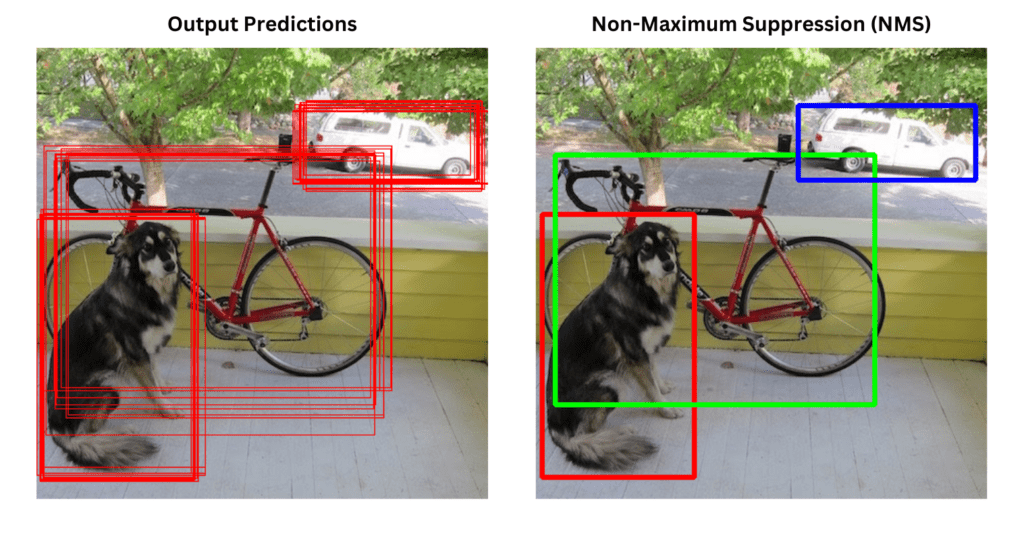
Algorithm Steps
- Sort all bounding boxes by their confidence score.
- Select the box with the highest confidence and remove it from the list.
- Compute IoU between this box and all others.
- Remove boxes with IoU above a threshold (e.g., 0.5).
- Repeat until no boxes remain.
Mathematical Intuition
Let be a box with score . You iterate over all boxes and apply:
Where is the suppression threshold.
Anchor Boxes
What are Anchor Boxes?
Anchor boxes (also called prior boxes) are predefined bounding boxes with different shapes and sizes. They allow object detectors to:
- Detect multiple objects in the same grid cell
- Handle aspect ratio and scale variation
Why Are They Needed?
Without anchor boxes, a single grid cell could detect only one object. But real-world scenes often contain overlapping or closely spaced objects.
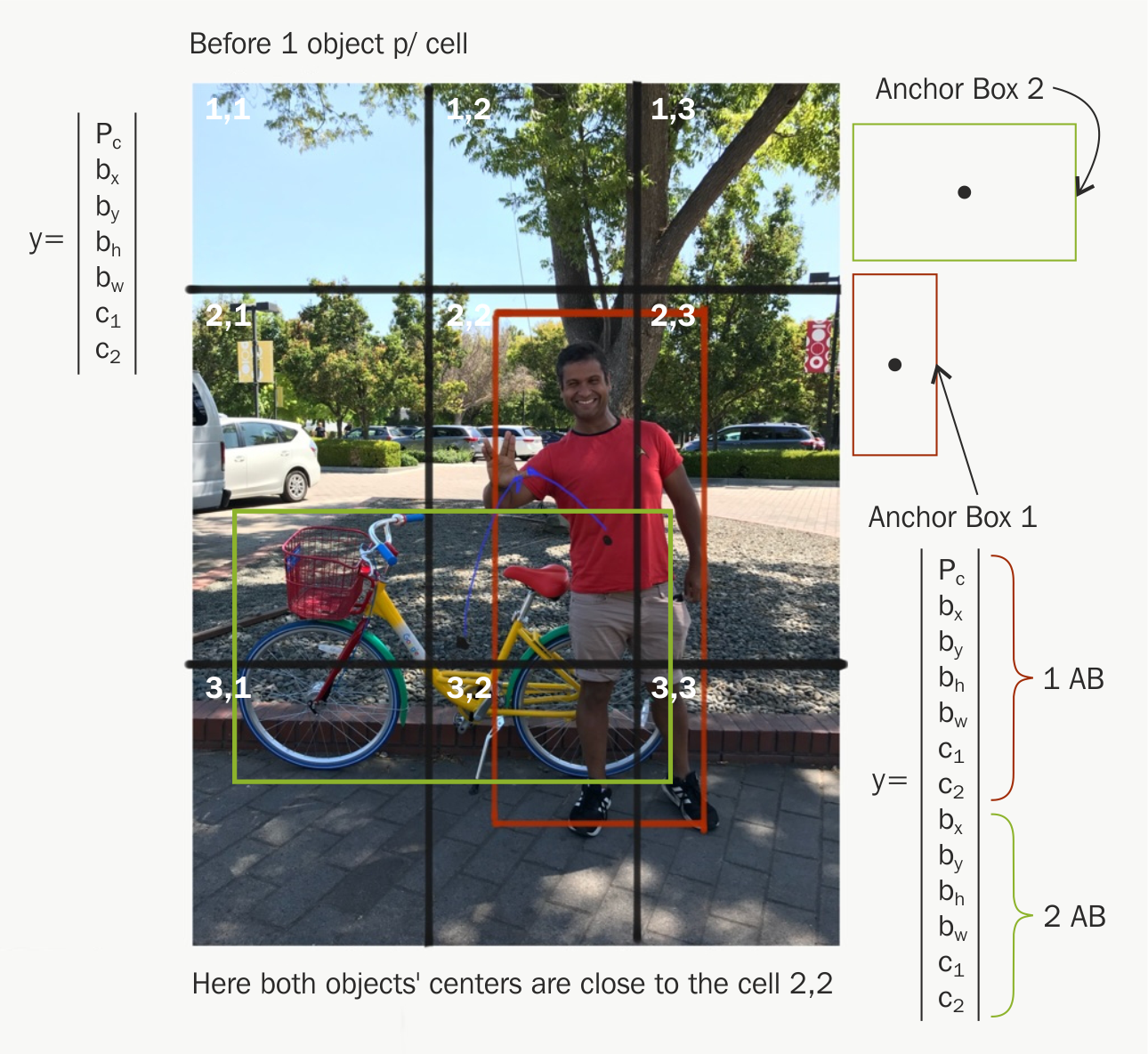
Anchor Box Design
You predefine anchor boxes per cell. Each one is defined by:
- Width
- Height
- Aspect ratio
For example, in SSD:
- 3 feature maps
- 6 anchors per feature cell
- 8732 total anchor boxes
Output Format with Anchors
For each anchor box, the network predicts:
- : offset from anchor center
- : log scale changes to width and height
- Confidence score
- Class probabilities
This transforms anchor box to the predicted box :
Summary
- IoU measures overlap and is used for loss/evaluation.
- Non-max suppression removes redundant boxes based on IoU.
- Anchor boxes allow detection of multiple objects at different scales/aspect ratios.
Together, these techniques form the foundation of modern object detection pipelines like YOLO, SSD, and Faster R-CNN.